BECE 2021 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Which of the following substances is a compound?
Solution: Water (H₂O) is a compound because it consists of two different elements (hydrogen and oxygen) chemically bonded together. Oxygen, magnesium, and sodium are all elements.
2. An atom of an element has a neutral charge because the
Solution: An atom is neutral when the number of protons (positive charge) equals the number of electrons (negative charge), balancing the overall charge.
3. Which of the following organisms is an ecto-parasite of animals?
Solution: Fleas are ecto-parasites because they live on the outside of their host (e.g., skin). Tapeworms, liver flukes, and roundworms are endo-parasites (live inside the host).
4. An atom has 20 nucleons and 9 protons. What is its neutron number?
Solution: Neutron number = Nucleons (total) - Protons = 20 - 9 = 11.
5. Which of the following statements about aerobic and anaerobic respiration is not correct?
Solution: Water is produced in aerobic respiration, not anaerobic. Anaerobic respiration produces alcohol (in yeast) or lactic acid (in muscles).
6. An aluminium cube of side 2 m has a mass 24 kg. Determine the density of the aluminium.
Solution: Density = Mass/Volume. Volume = side³ = 2 × 2 × 2 = 8 m³. Density = 24 kg / 8 m³ = 3 kg m⁻³.
7. An example of the process of osmosis is
Solution: Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Selective reabsorption in kidneys involves osmosis.
8. What is the systematic name of the compound CO?
Solution: CO is carbon(II)oxide because carbon has an oxidation state of +2 in this compound.
9. Which of the following methods can be used to prevent iron from rusting?
Solution: Painting, alloying, and keeping iron dry (desiccator) prevent rust. Moisture accelerates rusting.
10. The proper way of maintaining soil structure and fertility is termed as soil
Solution: Soil conservation involves practices to maintain soil fertility and structure.
11. The instrument that can be used to measure accurately the mass of a substance is
Solution: A beam balance measures mass by comparing unknown mass to known masses.
12. Which of the following chemical symbols can be used to remove permanent hardness of water?
Solution: Sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) removes permanent hardness by precipitating calcium/magnesium ions.
13. Which of the following chemical symbols is that of an element with seven electrons in the outermost shell?
Solution: Chlorine (Cl) has atomic number 17, so its electron configuration is 2,8,7 (7 valence electrons).
14. Which of the following statements about the base of a transistor are correct? The base is
Solution: The base is thin and activates the transistor. It can be p-type or n-type.
15. Which of the following instruments is connected in parallel across a resistor in an electrical circuit?
Solution: A voltmeter measures potential difference and is connected in parallel.
16. Which of the following fruits is dispersed by water?
Solution: Coconuts float and are dispersed by water due to their fibrous husk.
17. A farming system which involves the growing of rice and the rearing of fowls is known as
Solution: Mixed farming combines crop cultivation and livestock rearing.
18. Which of the following activities are cultural practices in vegetable production?
Solution: Fertilizer application and mulching are cultural practices. Harvesting is not.
19. The function of the white blood cells in humans is to
Solution: White blood cells defend against pathogens by producing antibodies and phagocytosis.
20. Mosquito pupa breathes through tubes called
Solution: Mosquito pupae use a siphon (breathing tube) to obtain air from the water surface.
21. An advantage of practicing organic farming is that it
Solution: Organic farming uses natural compost/manure, improving soil fertility.
22. Which of the following planets is at the centre of the solar system?
Solution: The Sun is the center of the solar system; others orbit it.
23. Determine the potential energy of a block of mass 2 kg placed on a building 10 m tall. [g=10 m s⁻²]
Solution: P.E. = mgh = 2 × 10 × 10 = 200 J.
24. Which of the following organisms attacks crops in storage?
Solution: Weevils infest stored grains/crops.
25. One of the properties of acids is that they
Solution: Acids turn blue litmus red.
26. The instrument used to measure potential difference across a resistor is
Solution: A voltmeter measures potential difference (voltage).
27. A machine lifts a load of 100 N through a vertical distance of 2 m in 10 s. What is the work done by the machine?
Solution: Work = Force × Distance = 100 N × 2 m = 200 J.
28. What is the power of the machine?
Solution: Power = Work/Time = 200 J / 10 s = 20 W.
29. Which of the following elements is a macro-nutrient of plants?
Solution: Sulphur is a macro-nutrient; others are micro-nutrients.
30. When an atom loses an electron, the ion formed is called
Solution: Loss of electrons forms a positively charged cation.
31. Which of the following chemical equations is balanced?
Solution: Option D has equal atoms of each element on both sides.
32. Purple colouration of leaves of plant is a major symptom of deficiency in
Solution: Phosphorus deficiency causes purple/reddish leaves.
33. Which of the following diseases is not a deficiency disease?
Solution: Cholera is caused by bacteria; others are due to nutrient deficiencies.
34. In an experiment to determine the various particle sizes of soil by sedimentation, the particles above clay suspension are
Solution: Silt particles settle above clay but below sand/gravel.
35. A person urinates more often in the rainy season than in the dry season because
Solution: Less sweating in rainy season leads to more urine production.
36. Heat from the sun is transferred by
Solution: Solar heat travels via radiation (vacuum of space).
37. Which of the following machines are complex machines?
Solution: All are complex machines (combine simple machines).
38. Calcium oxide and water react to form calcium hydroxide. The formula for the product is
Solution: Calcium hydroxide has the formula Ca(OH)₂.
39. The current flowing through a resistor of resistance 10 ohms is 2.5 A. What is the potential difference between the two terminals of the resistor?
Solution: V = IR = 2.5 A × 10 Ω = 25 V.
40. If a soil is smooth and sticky, it means that the soil has a large amount of
Solution: Clay particles are fine, making soil smooth and sticky when wet.
SECTION A
Answer All Of Question 1 and any TWO from SECTION B
1. (a) The diagrams below are illustrations of a set-up used to study the conditions for seed germination. The flasks are kept at 25°C during the experiment. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
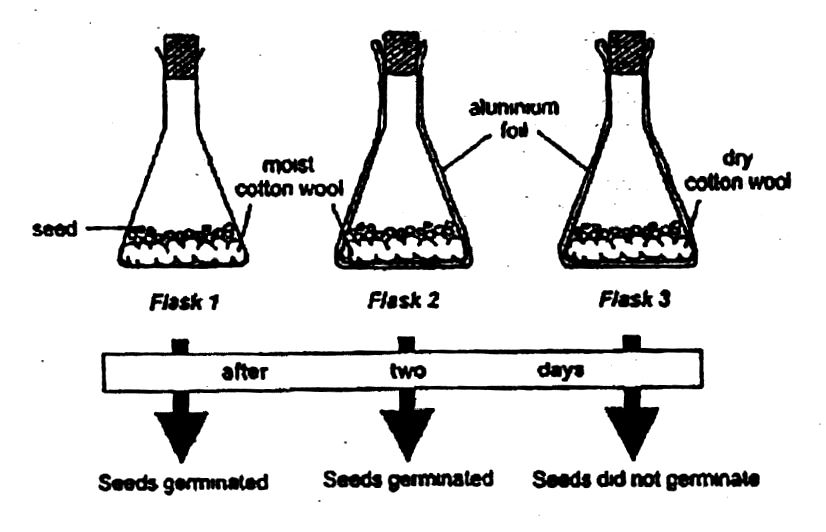
(i) What conclusion can be drawn from the results of flask 1 and flask 2?
(ii) What conclusion can be drawn from the results of flask 2 and flask 3?
(iii) The seedlings in flask 2 died after two weeks. What can be the reasons for this occurrence?
(iv) A candidate concluded that light was an important factor for the germination. Did the candidate make a correct conclusion?
(v) Give a reason for the answer stated in (iv) and state which of the flasks in the experiment could be used to support your answer.
(b) The diagram below are illustrations of an experimental set-up. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
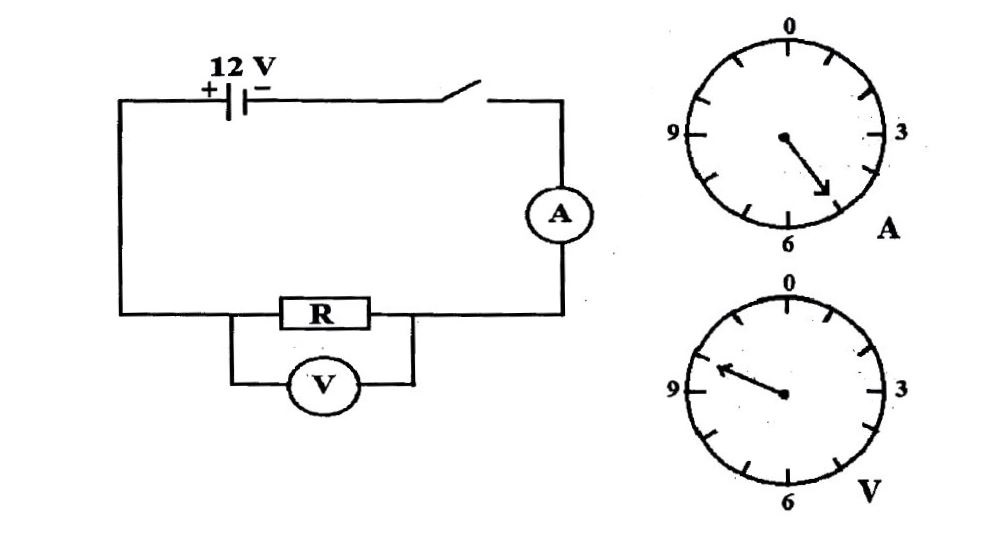
(i) Name the measuring instrument that is in:
(α) parallel;
(β) series
With the resistor R.
(ii) What quantity does each of the named instruments in (i) measure?
(iii) Read and record the values as indicated on:
(α) A in amperes;
(β) V in volts.
(iv) Use the values read in (iii) to calculate the value of R.
(v) State one precaution to be taken in performing this experiment.
(c) The diagrams below are illustrations of soil. Study the illustrations carefully and answer the questions that follow.
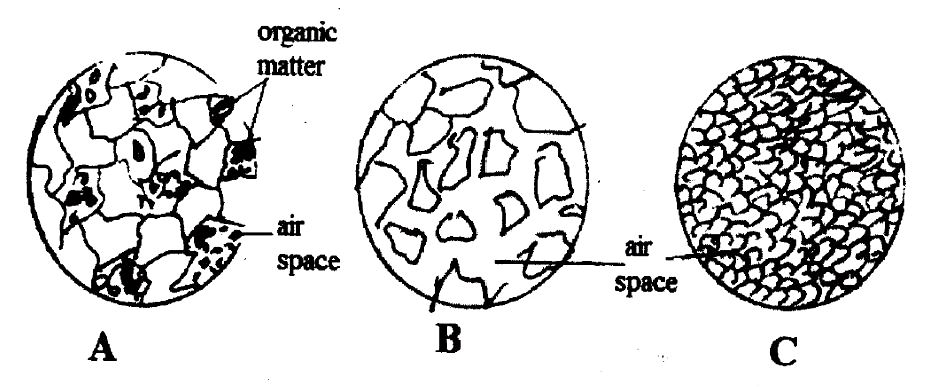
(i) Identify each of the soil types labelled A, B, and C.
(ii) Describe each of the soils under the following properties:
(α) Particle size
(β) Air space
(iii) Suggest two ways of improving soil type B for vegetable cultivation.
(d) The diagrams below is a set-up for preparation of common salt in the laboratory. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
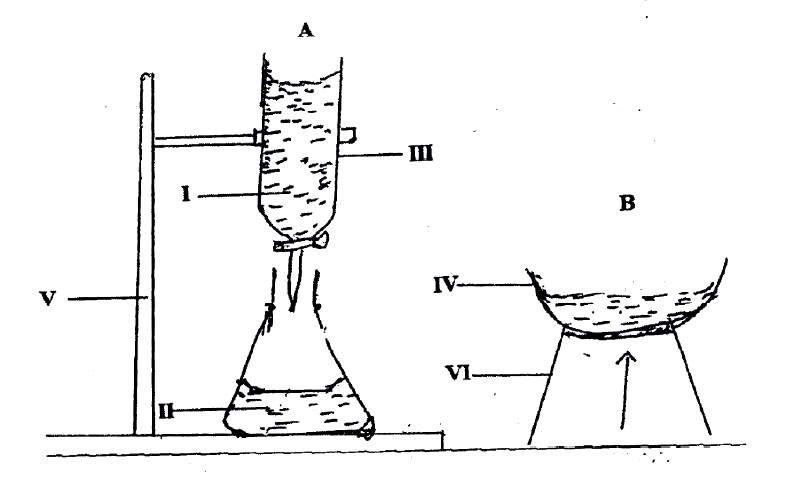
(i) Name each of the parts labelled IV, V, and VI.
(ii) Name two possible solutions that can react to produce salt.
(iii) Name the process that takes place when the two solutions named in (ii) react.
(iv) Name the process that takes place in the set-up B.
(v) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between the two solutions named in (ii).
Solution:
(a) Seed Germination Experiment
(i) Conclusion from flask 1 and flask 2:
Light is not necessary for germination.
(ii) Conclusion from flask 2 and flask 3:
Water is necessary for germination.
(iii) Reasons for dead seedlings in flask 2:
The food stored in the seed is used up.
The seedlings cannot carry out photosynthesis (no sunlight).
Lack of water/moisture.
(iv) Correctness of candidate’s conclusion:
No, the candidate made a wrong conclusion.
(v) Reason and supporting flask:
Light is not necessary for the germination of seed.
The seed in flask 2 germinated even though the flask was lined with aluminium foil (no light).
(b) Electrical Circuit Experiment
(i) Measuring instruments:
(α) Parallel: Voltmeter
(β) Series: Ammeter
(ii) Quantities measured:
Voltmeter: Potential difference/voltage
Ammeter: Electric current
(iii) Recorded values:
(α) A = 5 A
(β) V = 10 V
(iv) Calculation of R:
R=V/I=10/5=2Ω
(v) Precaution:
Ensure all electrical connections are tight.
Use properly calibrated voltmeter and ammeter.
Insert the key only while taking readings.
(c) Soil Types and Properties
(i) Identification of soil types:
A: Loamy soil / loam
B: Sandy soil / sand
C: Clayey soil / clay
(ii) Description of soil properties:
(α) Particle size:
A: Medium/large
B: Large/medium
C: Small
(β) Air space:
A: Moderate
B: Large
C: Small
(iii) Improving sandy soil (B) for vegetable cultivation:
Plant cover crops.
Apply organic manure/compost/farmyard manure/fertilizer.
Mulch the soil.
(d) Preparation of Common Salt
(i) Labelled parts:
IV: Evaporating dish
V: Clamp stand / retort stand
VI: Tripod stand
(ii) Possible solutions for salt production:
Sodium hydroxide
Hydrochloric acid
(iii) Process when solutions react:
Neutralization
(iv) Process in set-up B:
Evaporation / boiling / heating
(v) Balanced chemical equation:
HCl+NaOH→NaCl+H2O
SECTION B
Answer FOUR Questions only from This Section
2. (a) (i) State what happens when photosynthesis occurs in a leaf.
(ii) What is pollination?
(b) Explain briefly why the mass of lumpy charcoal remains unchanged when ground into powder but the mass of the same lump changes when heated to burn.
(c) (i) What is a physical quantity?
(ii) State two physical quantities.
(d) State two importance each of:
(i) light;
(ii) temperature;
In crop production.
Solution:
(a) Photosynthesis and Pollination
(i) What happens during photosynthesis in a leaf:
Glucose/starch is produced.
Oxygen is given out.
Carbon dioxide is used.
Water is used.
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll.
(ii) Pollination:
It is the transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same type.
(b) Charcoal Mass Change Explanation
Grinding lumpy charcoal (physical change):
The components remain unchanged; only the size/shape is altered.
Burning charcoal (chemical change):
Some components (e.g., carbon) are lost as gases (CO₂), reducing the mass.
(c) Physical Quantities
(i) Definition:
A property of a substance that can be measured.
(ii) Examples (any two):
Length
Mass
Time
Temperature
Electric current
Force
Density
(d) Importance in Crop Production
(i) Light:
Needed for photosynthesis (energy/starch production).
Affects fruit development and vegetative growth.
Absence leads to weak stems (etiolation).
(ii) Temperature:
High temperatures can scorch leaves.
Required for seed germination and plant growth.
Influences ripening of fruits.
Extreme temperatures cause water deficit (wilting).
3.(a) (i) What is hardness of water?
(ii) Give one example each of a natural source of water that is:
(α) hard water
(β) soft water
(b) What is the end-product of the digestion of each of the following?
(i) Meat
(ii) Cassava
(iii) Palm-oil
(c) Give one effect of each of the following factors considered in vegetable crop production:
(i) soil type
(ii) nearness to market
(iii) nearness to source
(d) (i) Explain briefly why an eclipse occurs.
(ii) Name the two types of eclipse.
Solution:
(a) Hardness of Water
(i) Definition:
The inability of water to lather easily with soap due to dissolved calcium/magnesium/iron(II) ions.
(ii) Natural sources:
(α) Hard water: Sea/ocean, well water, groundwater
(β) Soft water: Rainwater, river, snow
(b) Digestion End-Products
(i) Meat: Amino acids (ii) Cassava: Glucose (iii) Palm-oil: Fatty acids and glycerol
(c) Effects on Vegetable Crop Production
(i) Soil type:
Determines suitable crops for cultivation.
Affects water retention and nutrient availability.
(ii) Nearness to market:
Reduces post-harvest losses during transportation.
Ensures quick sale of perishable vegetables.
(iii) Nearness to water source:
Facilitates irrigation during dry seasons.
Eases pesticide/fertilizer application in liquid form.
(d) Eclipse
(i) Occurrence:
When the Sun's light is blocked by an opaque object (Moon/Earth), casting a shadow.
(ii) Types:
Solar eclipse (Sun obscured by Moon)
Lunar eclipse (Moon obscured by Earth's shadow)
4.(a) (i) Explain the term convection as applied to heat transfer.
(ii) Give two reasons why convection does not occur in solids.
(b) Give two effects of each of the following soil physical properties on maize cultivation:
(i) Texture
(ii) Water holding capacity
(c) Use any three of the following organisms to construct a food chain: Hawk, grasshopper, man, grass, toad, grasscutter
(d) (i) Consider the following elements and state which element(s) is/are metals: 1Na, 2N, 6C, 3Li
(ii) Explain briefly what is observed when pieces of each of the following metals are dropped into two separate test tubes each containing dilute hydrochloric acid:
(α) magnesium
(β) silver
Solution:
(a) Convection
(i) Definition:
Heat transfer in fluids where warmer (less dense) parts rise and cooler (denser) parts sink.
(ii) Why not in solids:
Particles are tightly bonded/fixed in position.
No fluid movement possible.
(b) Soil Properties and Maize Cultivation
(i) Texture:
Influences root penetration and aeration.
Determines nutrient retention capacity.
(ii) Water holding capacity:
Affects irrigation frequency.
Impacts drought resistance of crops.
(c) Food Chain Examples
Grass → grasshopper → toad
Grass → grasscutter → man
Grass → grasshopper → hawk
(d) Metals and Reactions
(i) Metals: Sodium (Na) and Lithium (Li)
(ii) Observations with HCl:
(α) Magnesium: Effervescence (hydrogen gas released)
(β) Silver: No reaction
5.(a) State two important components each of the soils that helps:
(i) Crops to grow well
(ii) To maintain good soil structure
(b) (i) Explain how energy in a windmill is obtained.
(ii) State one source of renewable energy.
(c) (i) Explain why steel is preferred to iron in building construction.
(ii) State two ways of preventing rusting.
(d) State three ways of preventing indigestion.
Solution:
(a) Soil Components
(i) For crop growth:
Nutrients/humus
Water
Air
(ii) For soil structure:
Organic matter/humus
Soil particles
Living organisms
(b) Windmill Energy
(i) Energy production:
Wind turns the windmill blades
The motion drives a turbine
Turbine converts kinetic energy to electrical energy
(ii) Renewable energy source:
Solar
Wind
Hydropower
(c) Steel vs Iron
(i) Preference for steel:
Higher tensile strength
More resistant to corrosion
Lighter than iron
(ii) Rust prevention:
Painting
Galvanizing
Oil/grease coating
(d) Preventing Indigestion
Eat slowly and chew properly
Avoid lying down immediately after eating
Limit spicy/fatty foods
Don't overeat
Avoid excessive alcohol
6.(a) State three ways by which the atmosphere in an industrial area is polluted.
(b) (i) Write the word equation for each of the following reactions between:
(α) calcium and oxygen
(β) nitrogen and hydrogen
(ii) State the hazard that could be prevented when each of the following protective materials are used in the laboratory:
(α) gas mask
(β) goggles
(c) If a cuboid of weight 100 N, has sides 5 cm by 10 cm, calculate the:
(i) Area of the cuboid
(ii) Pressure exerted by the cuboid when it lies on its side
(d) (i) Explain the term mixed farming.
(ii) State two advantages of mixed farming.
Solution:
(a) Industrial Air Pollution
Smoke/soot emissions
Exhaust fumes from vehicles
Release of poisonous gases (CO, SO₂)
Dust from factories
(b) Chemical Reactions & Safety
(i) Word equations:
(α) Calcium + oxygen → calcium oxide
(β) Nitrogen + hydrogen → ammonia
(ii) Protective equipment:
(α) Gas mask: Prevents inhalation of toxic gases
(β) Goggles: Protects eyes from chemical splashes
(c) Cuboid Calculations
(i) Area: = 5 cm × 10 cm = 50 cm²
(ii) Pressure: = Force/Area = 100 N / 50 cm² = 2 N/cm²
(d) Mixed Farming
(i) Definition:
Simultaneous cultivation of crops and rearing of livestock on the same land
(ii) Advantages:
Diversified income sources
Mutual benefits (manure for crops, crop residues for feed)
Better land utilization